SVG Images
Draw an SVG (see SVG Support).
If the root dimensions are in absolute units, the width/height properties have no effect since the initial viewport is fixed.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| svg | SVG | SVG Image. |
| width? | number | Width of the destination image. This is used to resolve the initial viewport when the root SVG width is specified in relative units. |
| height? | number | Height of the destination image. This is used to resolve the initial viewport when the root SVG height is specified in relative units. |
| x? | number | Optional displayed x coordinate of the svg container. |
| y? | number | Optional displayed y coordinate of the svg container. |
The ImageSVG component doesn't follow the same painting rules as other components.
see applying effects.
On Web, the Current Transformation Matrix (CTM) won't be applied to ImageSVG because the component relies on browser SVG rendering instead of CanvasKit. The SVG is rendered as a hidden image element and then imported as image data. This means transformations need to be prepared beforehand or applied through the Group component with explicit transform matrices.
Example
import {
Canvas,
ImageSVG,
useSVG
} from "@shopify/react-native-skia";
const ImageSVGDemo = () => {
// Alternatively, you can pass an SVG URL directly
// for instance: const svg = useSVG("https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/fd/Ghostscript_Tiger.svg");
const svg = useSVG(require("../../assets/tiger.svg"));
return (
<Canvas style={{ flex: 1 }}>
{ svg && (
<ImageSVG
svg={svg}
width={256}
height={256}
/>)
}
</Canvas>
);
};
You can also use an inlined string as SVG (using Skia.SVG.MakeFromString):
import React from "react";
import { Canvas, ImageSVG, Skia } from "@shopify/react-native-skia";
const svg = Skia.SVG.MakeFromString(
`<svg viewBox='0 0 290 500' xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'>
<circle cx='31' cy='325' r='120px' fill='#c02aaa'/>
</svg>`
)!;
export const SVG = () => {
return (
<Canvas style={{ flex: 1 }}>
<ImageSVG
svg={svg}
x={0}
y={0}
width={290}
height={500}
/>
</Canvas>
);
};
Text
Both Skia.SVG.MakeFromData and Skia.SVG.MakeFromString accept an optional second parameter to provide custom font management for text rendering in SVGs.
This works similarly to the Paragraph API where you can use the useFonts hook to load custom fonts:
import React from "react";
import { Canvas, ImageSVG, Skia, useFonts } from "@shopify/react-native-skia";
const SVGWithCustomFonts = () => {
const fontMgr = useFonts({
Roboto: [
require("path/to/Roboto-Regular.ttf"),
require("path/to/Roboto-Bold.ttf")
]
});
if (!fontMgr) {
return null;
}
const svg = Skia.SVG.MakeFromString(
`<svg viewBox='0 0 290 500' xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'>
<text x='10' y='50' font-family='Roboto' font-size='24'>Custom Font</text>
</svg>`,
fontMgr
)!;
return (
<Canvas style={{ flex: 1 }}>
<ImageSVG
svg={svg}
x={0}
y={0}
width={290}
height={500}
/>
</Canvas>
);
};
On Web, both the fontMgr parameter (second parameter) and image resources (third parameter) are ignored as SVG rendering relies on the browser's native SVG renderer rather than Skia's SVG module.
Images
Both Skia.SVG.MakeFromData and Skia.SVG.MakeFromString accept an optional third parameter to provide image resources for <image> elements in SVGs.
This works similarly to image loading in Skottie.
You can reference images either through base64 data URIs or by providing a resource map:
import React from "react";
import { Canvas, ImageSVG, Skia, useData } from "@shopify/react-native-skia";
const SVGWithImages = () => {
// Load an image asset
const logo = useData(require("path/to/image.png"));
if (!logo) {
return null;
}
// Option 1: Using base64 data URI (embedded)
const svgWithEmbeddedImage = Skia.SVG.MakeFromString(
`<svg width="200" height="200" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<image xlink:href="data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KG..." height="200" width="200" />
</svg>`
);
// Option 2: Using external reference with resource map
const svgWithExternalImage = Skia.SVG.MakeFromString(
`<svg width="200" height="200" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<image xlink:href="logo.png" height="200" width="200" />
</svg>`,
null,
{ "logo.png": logo }
);
return (
<Canvas style={{ flex: 1 }}>
<ImageSVG svg={svgWithExternalImage} x={0} y={0} width={200} height={200} />
</Canvas>
);
};
When rendering your SVG with Skia, all fonts available in your app are also available to your SVG.
However, the way you can set the font-family attribute is as flexible as on the web.
// ✅ This is really all that is supported:
<text font-family="MyFont" />
// ❌ This won't work. If MyFont is available, this syntax will be accepted.
// but it will never fallback to monospace
<text font-family="MyFont, monospace" />
// ❌ The single quote syntax won't work either.
<text font-family="'MyFont'" />
Scaling the SVG
As mentioned above, if the root dimensions are in absolute units, the width/height properties have no effect since the initial viewport is fixed. However you can access these values and use the fitbox function.
Example
In the example below we scale the SVG to the canvas width and height.
import React from "react";
import { Canvas, ImageSVG, Skia, rect, fitbox, Group } from "@shopify/react-native-skia";
const svg = Skia.SVG.MakeFromString(
`<svg viewBox='0 0 20 20' width="20" height="20" xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'>
<circle cx='10' cy='10' r='10' fill='#00ffff'/>
</svg>`
)!;
const width = 256;
const height = 256;
const src = rect(0, 0, svg.width(), svg.height());
const dst = rect(0, 0, width, height);
export const SVG = () => {
return (
<Canvas style={{ flex: 1 }}>
<Group transform={fitbox("contain", src, dst)}>
<ImageSVG svg={svg} x={0} y={0} width={20} height={20} />
</Group>
</Canvas>
);
};
Applying Effects
The ImageSVG component doesn't follow the same painting rules as other components.
This is because behind the scene, we use the SVG module from Skia.
However you can apply effets using the layer property.
Opacity Example
In the example below we apply an opacity effect via the ColorMatrix component.
import React from "react";
import { Canvas, ImageSVG, Skia, rect, fitbox, useSVG, Group, Paint, OpacityMatrix, ColorMatrix } from "@shopify/react-native-skia";
const width = 256;
const height = 256;
export const SVG = () => {
const tiger = useSVG(require("./tiger.svg"));
if (!tiger) {
return null;
}
const src = rect(0, 0, tiger.width(), tiger.height());
const dst = rect(0, 0, width, height);
return (
<Canvas style={{ flex: 1 }}>
<Group
transform={fitbox("contain", src, dst)}
layer={<Paint><ColorMatrix matrix={OpacityMatrix(0.5)} /></Paint>}
>
<ImageSVG svg={tiger} x={0} y={0} width={800} height={800} />
</Group>
</Canvas>
);
};
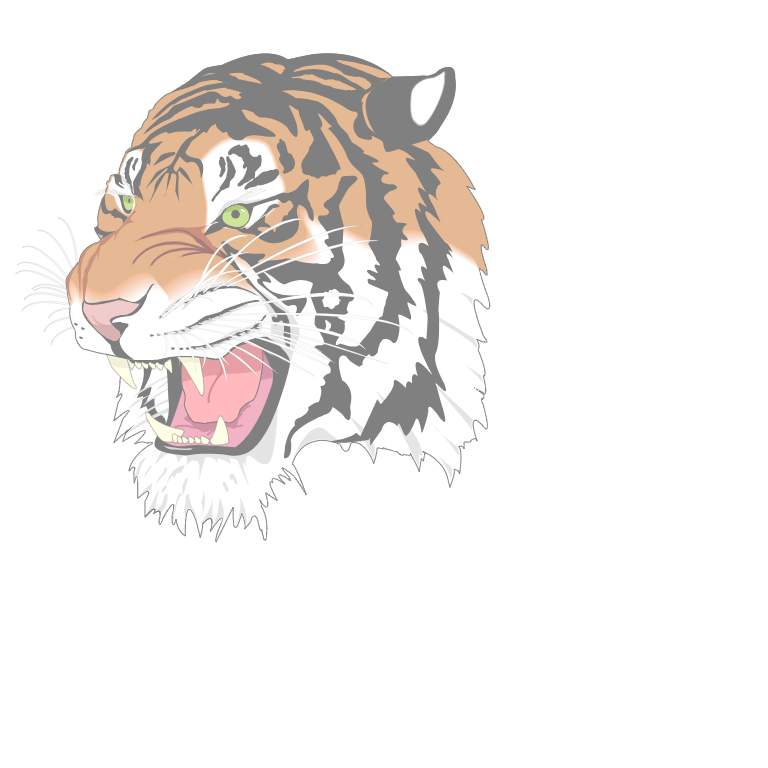

Blur Example
In the example below we apply a blur image filter to the SVG.
import React from "react";
import { Canvas, ImageSVG, Skia, rect, fitbox, useSVG, Group, Paint, Blur } from "@shopify/react-native-skia";
const width = 256;
const height = 256;
export const SVG = () => {
const tiger = useSVG(require("./tiger.svg"));
if (!tiger) {
return null;
}
const src = rect(0, 0, tiger.width(), tiger.height());
const dst = rect(0, 0, width, height);
return (
<Canvas style={{ flex: 1 }}>
<Group transform={fitbox("contain", src, dst)} layer={<Paint><Blur blur={10} /></Paint>}>
<ImageSVG svg={tiger} x={0} y={0} width={800} height={800} />
</Group>
</Canvas>
);
};
Result

SVG Support
The SVG module from Skia displays SVGs as images. We expect most SVG files to render correctly out of the box, especially if they come from Figma or Illustrator. However, please be aware of some of the quirks below when using it. Text elements currently won't render and any external XML elements such as XLink or CSS won't render. If your SVG doesn't render correctly and you've considered all the items below, please file an issue.
CSS Styles
CSS styles included in SVG are not supported.
A tool like SVGO can help with converting CSS style attributes to SVG attributes if possible.
You can use it online here.
For instance, it can normalize CSS style attributes that contain transformations to the proper transform property.
RGBA Colors
The RGBA color syntax is not supported. Instead, it would help if you used the fill-opacity and stroke-opacity attributes. Consider the example below.
<circle
r="10"
cx="10"
cy="10"
fill="rgba(100, 200, 300, 0.5)"
stroke="rgba(100, 200, 300, 0.8)"
/>
Would need to be rewritten as:
<circle
r="10"
cx="10"
cy="10"
fill="rgb(100, 200, 300)"
fill-opacity="0.5"
stroke="rgb(100, 200, 300)"
stroke-opacity="0.8"
/>
The opacity attribute also applies to both the fill and stroke attributes.
Non Supported Elements
Below is the list of non-supported element.
<animate><feComponentTransfer><feConvolveMatrix><feTile><feDropShadow><foreignObject><script><view>
Inlined SVGs
Some SVGs contain inlined SVGs via the <image> or <feImage> elements. This is not supported.
Gradient Templates
The deprecated xlink:href attribute is not supported in gradients.
You can use the href attribute instead.
However, we found that it doesn't appear to be adequately supported.
We would recommend avoiding using it.
Fallbacks
Some SVGs with issues display nicely in the browser because they are very tolerant of errors. We found that the Skia SVG module is much less forgiving.